Mastopexy (Breast lift)
Ptosis can be defined as the prolapse of a structure at a level below what would be considered optimal for its normal appearance or function. In the breast, ptosis refers to a laxity of skin in the breast area that causes the mammary gland it contains to adopt a form that is lower and altered, which is principally an aesthetic concern since function is not impaired. (When the volume of the breast and its associated cutaneous cover are excessive, breast reduction is the indicated procedure).
Candidates. Most patients have had two or three children and are between 30 and 40 years of age, however some women may be younger and in some cases may have never been pregnant, others experience sagging breasts following weight loss. Dermal mastopexy can be performed at any age and while not recommended during pregnancy or shortly after delivery, this surgery does not alter the regular functions of the breast and allows lactation if required.
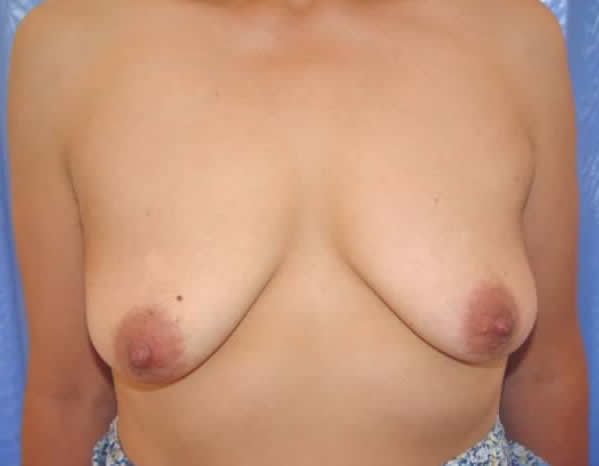
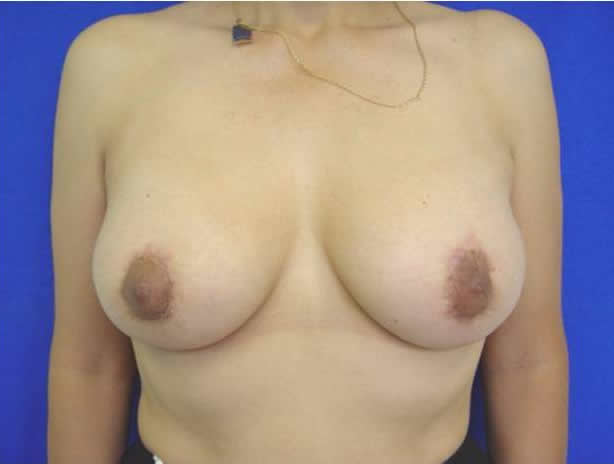
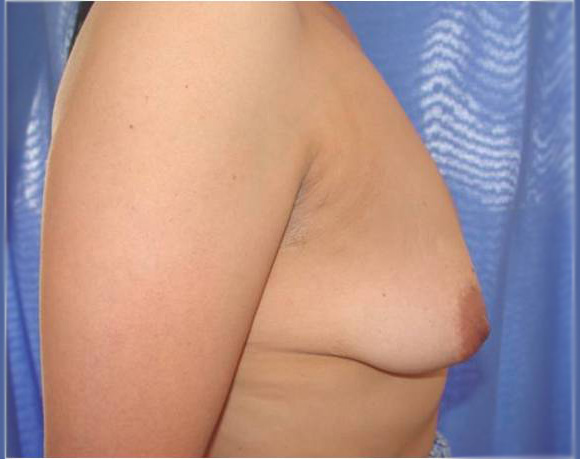
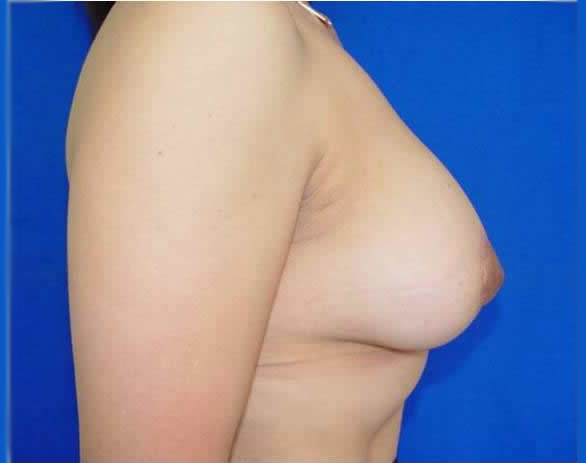
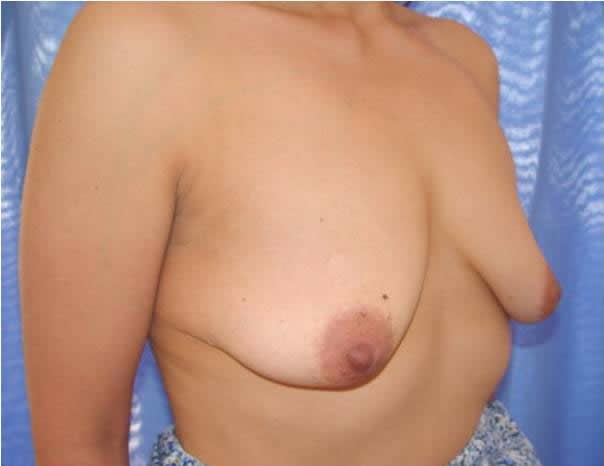
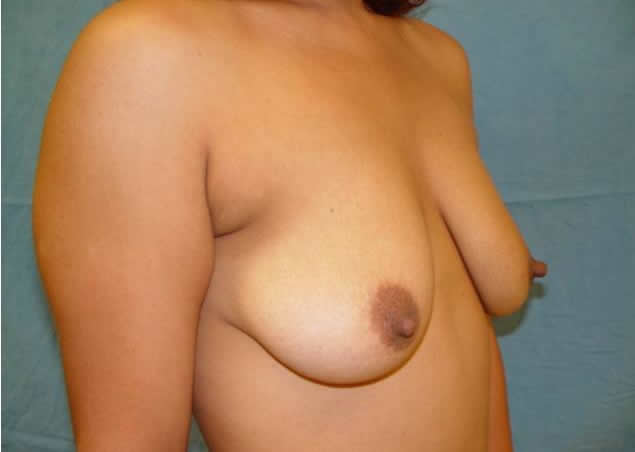
Surgery. When the volume of the breast is less than optimal and there is some laxity of the skin, the appropriate surgical correction is the placement of an implant or augmentation mammoplasty. When the volume of the breast is adequate but has been displaced by excessive cutaneous cover, the operation should include the removal of excess skin, the lifting of the nipple areolar complexes, adjustment of skin in the lower portion of the breast and the readjustment of the form and position of the mammary tissue and its contents. In mild cases in which there is loose skin and a lack of volume in the mammary tissue, this correction can be achieved by adjusting the skin around the areolae (periareolar technique) and inserting a moderately sized implant (periareolar mastopexy with implants), but in moderate to severe cases the adjustment of the skin will leave a scar in the form of an inverted T ("anchor-shape") of which the patient should be aware, although we always try to make this incision as short as possible, and the scar tends to disappear with time. In most cases general anesthesia is used, although the procedure may be done under local anesthesia and intravenous sedation.
Postoperative care. Recovery is usually rapid, the patient remains in the clinic for 2 to 3 hours and goes home that same evening. Analgesics and anti-inflammatories are prescribed initially and rest for one week. The stitches are removed in 10 days at which point the patient may resume regular activities, although upper-body exercises should be avoided for 8 weeks, and a special lycra garment worn for that same amount of time.
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
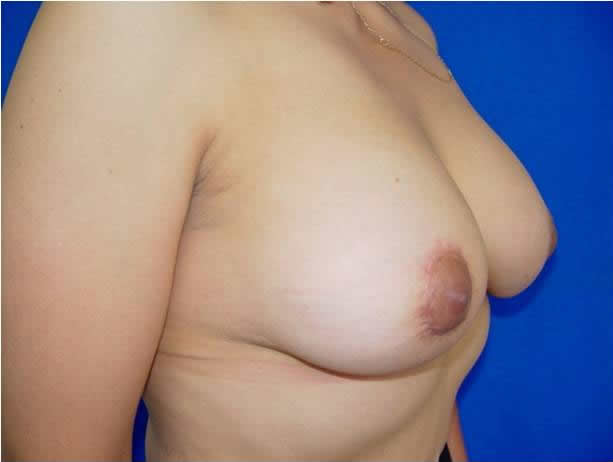 |
Before and after surgery, periareolar mastopexy with implants
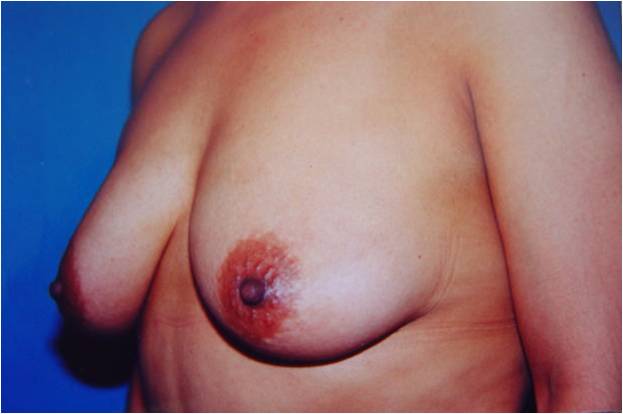 |
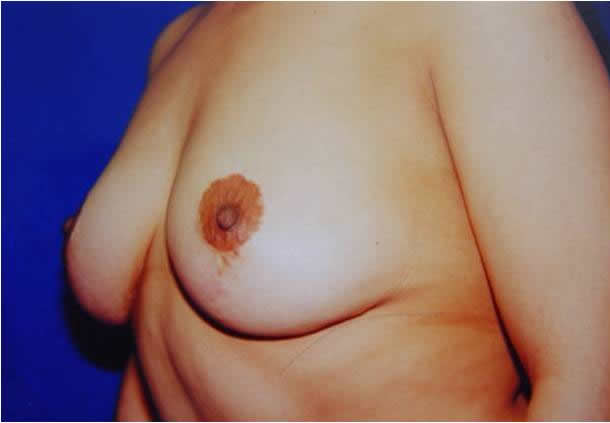 |
|
 |
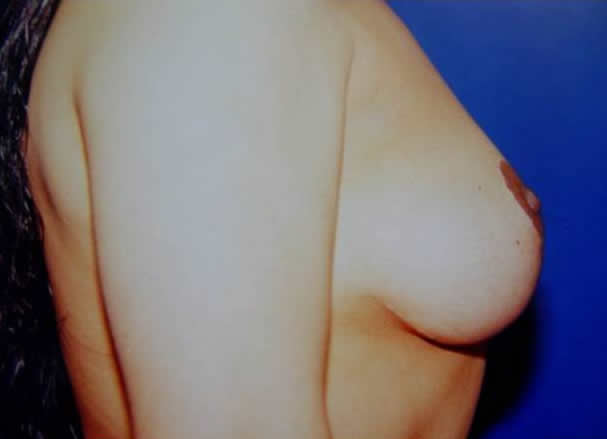 |
|
 |
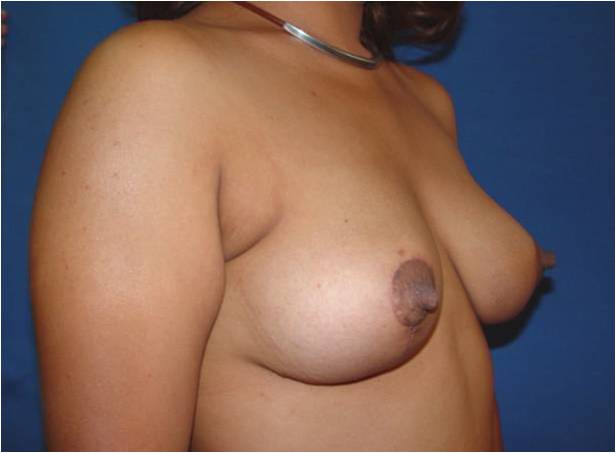 |
Before and after surgery, periareolar mastopexy with inverted T incision.